Electric well pumps are essential for a variety of applications, especially for extracting water from wells. These pumps are powered by electricity and are commonly used in both residential and industrial settings to supply water for irrigation, drinking, and other processes.
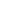
Vertical submersible pumps are designed to be submerged in the water source, making them ideal for deep-well applications. The pump is positioned vertically within the well, and the motor is located at the top of the pump unit. This setup allows for efficient water extraction from deep wells, where the water level may be located far below the surface.

One of the key advantages of vertical submersible pumps is their ability to handle high-pressure applications. Since the pump is submerged, it is also well-suited for situations where the water needs to be pushed over long distances or at elevated heights. This is common in agricultural irrigation systems, where water must be moved from deep wells to crop fields.
Another benefit of vertical submersible pumps is their ability to operate quietly and efficiently. These pumps are typically more energy-efficient compared to other types of pumps, making them cost-effective for long-term use. They are also durable, with a longer service life when properly maintained, as the submerged design reduces the likelihood of wear and tear from environmental factors.
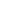
Pneumatic submersible pumps are a different type of submersible pump that uses compressed air to operate. These pumps are often used in applications where electrical power is unavailable or unsuitable, such as in hazardous environments or remote locations. Pneumatic submersible pumps work by using the force of compressed air to drive the pump's motor, which then moves water from the well.
One of the primary advantages of pneumatic submersible pumps is their versatility in various settings. They can be used in locations where electrical power is limited or not available, such as in construction sites, mining operations, or offshore drilling rigs. Additionally, since these pumps do not require electricity, they are safer in environments where sparks or electrical hazards could be a concern, such as in volatile chemical processing plants.
Pneumatic submersible pumps are also relatively easy to maintain, as they have fewer components that can wear out compared to electric pumps. They are ideal for use in applications that require pumping water from moderate to shallow depths. However, their performance can be influenced by the availability and pressure of compressed air, so ensuring an adequate air supply is critical to their operation.
While both vertical submersible pumps and pneumatic submersible pumps are used for similar purposes, there are key differences between them. Vertical submersible pumps are powered by electricity and are ideal for deep-well applications, offering high pressure and efficient energy use. They are typically used in applications that require continuous and reliable operation over long periods.
Pneumatic submersible pumps, on the other hand, are powered by compressed air and are ideal for use in remote locations or hazardous environments where electricity might not be available or safe to use. These pumps are versatile, easy to maintain, and offer a reliable solution in areas where electrical pumps may not be feasible.
Electric well pumps, including vertical submersible pumps and pneumatic submersible pumps, are essential tools for efficiently extracting water in various industrial, agricultural, and residential applications. Vertical submersible pumps offer efficiency and durability for deep-well applications, while pneumatic submersible pumps provide a versatile and safe alternative when electrical power is not an option.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى